How to Diagnose and Manage Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Simple Guide
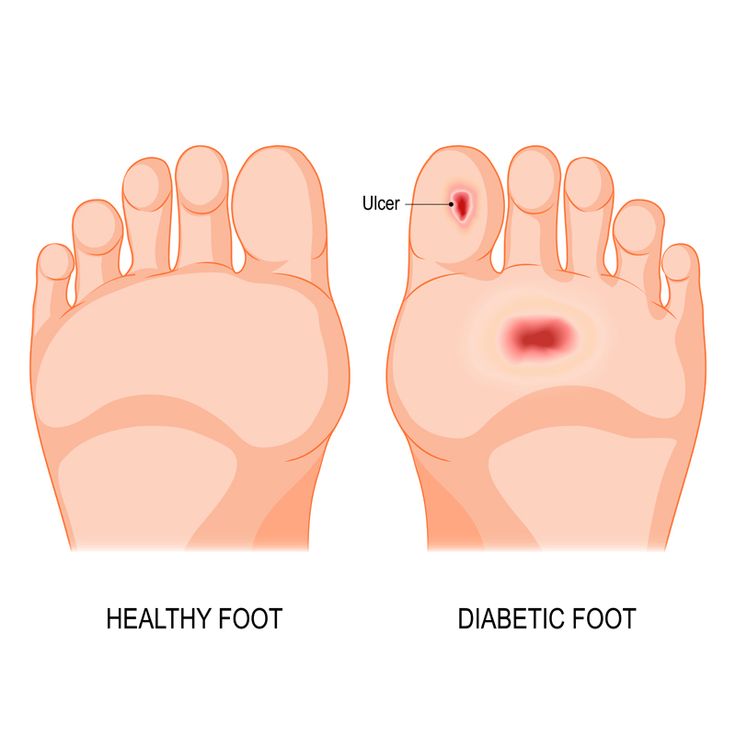
What Is a Diabetic Foot Ulcer?
- Neuropathic ulcers: Caused by nerve damage and loss of sensation.
- Ischemic ulcers: Occur due to poor blood supply to the foot.
- Neuro-ischemic ulcers: Involve both nerve damage and poor circulation.
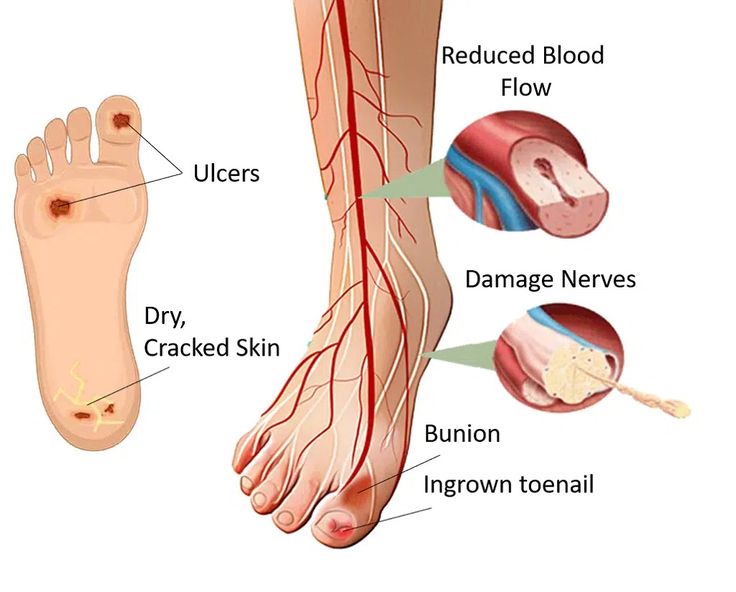
Early Signs and Symptoms
- Swelling, redness, or warmth around a wound
- Persistent foot pain or numbness
- Fluid drainage or foul smell from a sore
- Black or discolored skin ( Gangrene )
- A wound that doesn’t heal within a few days
How Is a Diabetic Foot Ulcer Diagnosed?
- Physical examination: Checking wound depth, infection, and tissue condition.
- Doppler ultrasound: Measures the flow of blood in the leg arteries.
- Angiography: Detects narrowed or blocked blood vessels.
- Wound culture: Identifies bacteria causing infection.
- Blood sugar tests: Ensures glucose control for better healing.
Treatment and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- Regular cleaning and dressing of the ulcer
- Use of antiseptic or medicated dressings
- Removal of dead or infected tissue (debridement) to speed up recovery
- Oral or Intravenous Antibiotic therapy required depending on the severity.
- Proper foot hygiene and dressing changes are essential to stop the spread of bacteria.
- Peripheral Angioplasty: A minimally invasive procedure to open blocked arteries using a small balloon or stent.
- Bypass surgery: Redirects blood flow around blocked arteries to improve oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Use of specialized footwear or diabetic shoes
- Orthotic insoles to balance weight
- Avoiding long walks or barefoot movement
- Keep blood sugar levels under control.
- Quit smoking—it reduces blood flow and delays healing.
- Eat a diet rich in protein, vitamins, and fiber.
- Exercise regularly (under medical guidance).
Role of a Vascular Surgeon in Diabetic Foot Care
- Identifying narrowed or blocked arteries
- Performing angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery
- Treating infections caused by poor circulation
- Preventing amputation by saving the affected limb
Prevention Tips for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- Inspect your feet daily for cuts or swelling.
- Wash your feet with lukewarm water and mild soap.
- Trim toenails carefully to avoid ingrown nails.
- Wear clean, comfortable socks and well-fitted shoes.
- Moisturize your feet (avoid applying lotion between toes).
- Keep your blood sugar and cholesterol levels in check.
- Get routine foot examinations by a vascular or diabetic foot specialist.
When Should You See a Doctor?
- Non-healing wounds or open sores
- Pain, swelling, or change in foot color
- Foul odor or pus discharge
- Numbness or tingling sensations
Conclusion
FAQs
1. What is the main cause of diabetic foot ulcers?
They occur due to a combination of nerve damage and reduced blood flow caused by prolonged high blood sugar.
2. How long does it take for a diabetic foot ulcer to heal?
Healing may take several weeks or months depending on blood circulation and infection control.
3. Can a diabetic foot ulcer heal naturally?
Minor ulcers can heal with proper care, but severe ones require medical attention and vascular evaluation
4. What happens if a diabetic foot ulcer is left untreated?
It may lead to infection, tissue death (gangrene), and in severe cases, amputation.
5. How can I prevent diabetic foot ulcers in the future?
Maintain stable blood sugar levels, wear protective shoes, and check your feet daily for early signs of injury.
